What is water?
Hardly any industrial manufacturing process can do without water treatment. But not all pure water is the same.
Which components of water cause problems for us users, and what’s behind the different treatment options?
Water is an excellent coolant and a universal solvent in which almost all substances are soluble. Depending on the activity and concentration of positively or negatively charged salts, water can be acidic or alkaline (basic).
Did you know that dissolved salts in water occur as ions (anions -/cations+) and can be removed from the water by means of ion exchange (deionisation)? This deionised water is called DI water.
Conductance is an indicator of the “pollution” in the water. Water is only conductive when salts are dissolved in it. Its salinity is determined by means of conductivity measurement. Since the electric current is transported by dissolved salts (ions), conductivity increases in parallel with ion concentration.
Did you know that conductivity is the reciprocal of the electrical resistance R?
At easymetal, we specialise in the removal of substances from water. With over 20 years of experience, we cover a broad spectrum of water treatment in metal processing with our 3 product areas: reverse osmosis (EASYRO®), deionisation (E.KO IONISER®) and disinfection (henndrixx®).
We offer the optimal water treatment process, depending on the required degree of purity. Individual requirements may also demand a combination and possible adaptation of the individual products. We work very closely with our OEM partners throughout the EU and can thus respond to every individual requirement.
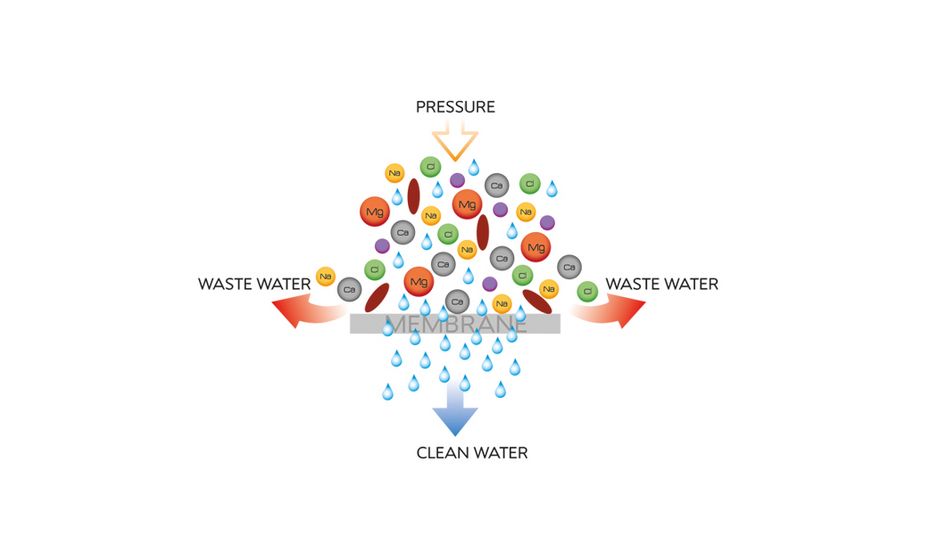
Did you know that reverse osmosis is a pressure-driven membrane process (mechanical-physical filtration) in which the smallest molecules, germs and ions are almost completely separated from a solution (e.g., water)?
State-of-the-art reverse osmosis systems have a filtration efficiency of up to 99% based on a 2000 ppm NaCl solution and a conductivity result of 1-50 µs/cm.
Did you know that a water molecule measures 5 Ångstroms in diameter?
In our EASYRO® reverse osmosis system, the water is forced through a TFC high-grade high-performance membrane with a mesh size of only 6 Ångstrom (Å). Salts and other residues are filtered out. The input conductance of the water is thus reduced by up to 98%.
Did you know that the degree of purity of deionised water (ultrapure water) depends on its conductance?
The lower the conductance, the higher the degree of purity.
Ultrapure water 0.1 - 1 µs/cm
High purity water 0.055 - 0.1 µs/cm
We have developed a patented process for deionisation that makes it possible to produce the purest DI water and at the same time meet the high environmental standards.
Originally, the E.KO IONISER® was developed especially for the water treatment of wire eroding machines.
The E.KO IONISER® guarantees an optimum pH value with the lowest conductance of up to 0.1 µs over the running time of the entire machine. In the meantime, the field of application has expanded, as these quality requirements are also demanded in other metal processing applications.
Did you know that pre-deionisation increases service life and ensures process stability?
High requirements in metal processing
In metal processing the processes are becoming increasingly complex, which means that the demands on water treatment are becoming ever higher. The decisive parameters for the assessment of water quality in metal processing are predominantly:
hardness components, silicate (silicic acid), chloride, metal salts, pH value, conductance, turbidity and organic substances (bacteria, germs, algae, ...)
Did you know that the positively (+) charged cations include, e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium and silicate, and the negatively (-) charged anions include, e.g., chloride, sulphate, nitrate and phosphate?
The best treated DI water has a very low conductance. In parts cleaning, the purity of the DI water is crucial for the optimum rinsing process before the subsequent coating. The smallest residues can severely impair the coating result.
Optimal water treatment is also of great importance for the preparation of cooling lubricants.
When preparing an emulsion with untreated water, these dissolved salts (hardness components, sulphates, chlorides, etc.) now enter the cooling circuit. Due to the heating and evaporation process, the emulsion is enriched with the salts remaining in the cooling circuit. This leads to an undesirable increase in salinity.
High salt loads can leave white deposits and residues on the workpieces. Chlorides in the cooling lubricant lead to corrosion on workpieces and to the formation of stains on aluminium.
Did you know that the salinisation of the cooling lubricant is mostly caused by evaporation and evaporation losses?
Salts cannot evaporate, but remain in the cooling lubricant and become more and more concentrated. Depending on the running time and evaporation, the water content quickly halves and the total salt content doubles.
Mains water is not sufficient for refilling, not even with water softening.
Softened water from cation exchangers has approximately the same salt content as the original mains water. Salinisation therefore still occurs via the drinking water feed. Salinisation can only be avoided by using DI water in the fluid management. DI water no longer contains any dissolved salts, except for traces, and therefore does not allow any salinisation from the outset.
Did you know that in the erosion process, the water in the machine should be changed at least once a year?
Do you have any questions on the topic? Contact us, we will be happy to advise you.